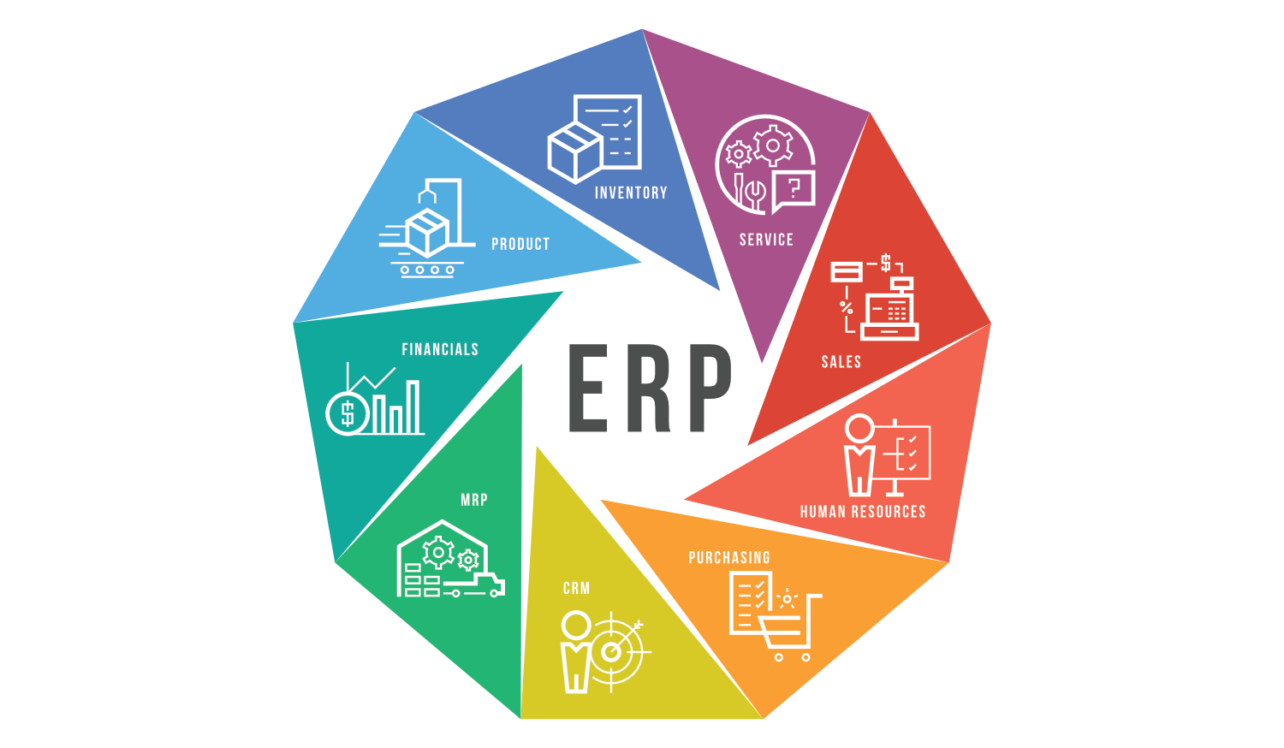
In its essence, the ERP system consists of incorporated modules which are used by the business to gather, store, manage and interpret data for many (ideally all) of its activities.
Some of the ERP modules are:
- Commercial management
- Financial management
- Invoicing
- Retail management
- Product planning
- Production management
- Service management
- Financial accounting
- Sales
- Marketing
- Revenue-Expenses
- General ledger
- Fixed asset management
- Warehouse management
- Payroll
- Distribution management
- Supply chain management
- Human resources management (HRM)
- Client Relationship management (CRM)
This structure offers enormous flexibility in an ERP solution, since the solution itself is adapted every time according to the needs of the client.
For instance, a store that focuses only in product sales can install only the modules that meet its specific needs such as accounting, warehouse management and orders. On the other hand, a factory needs modules such as production management, raw materials management and supplier management.
It is worth noting that each company’s needs differ, even between companies operating in the same industry.